Solve a Square Linear System Using Gaussian Elimination (In-Line)
This is a part of the student software manual project for Math 5610: Computational Linear Algebra and Solution of Systems of Equations.
Routine Name: direct_ge_bsin
Author: Christian Bolander
Language: Fortran. This code can be compiled using the GNU Fortran compiler by
$ gfortran -c direct_ge_bsin.f90
and can be added to a program using
$ gfortran program.f90 direct_ge_bsin.o
Description/Purpose: This routine uses in-line versions of the subroutines mat_row_ech and backsub to solve a square linear system of equations such as
using Gaussian elimination to reduce the augmented coefficient matrix to row echelon form and then apply the backward substitution method to find an approximate solution for x. Since the row echelon form conversion and backward substitution are done in-line, this Gaussian Elimination method is much faster than direct_ge_bs. The augmented coefficient matrix is defined by
The Gaussian elimination process computes the action of the inverse of A on b.
Input:
m : INTEGER - number of rows in the augmented coefficient matrix A (corresponds to the length of the solution vector x)
n : INTEGER - number of columns in the augmented coefficient matrix A (includes the square matrix x as well as the )
aug_A : REAL - augmented coefficient matrix of size m x n
Output:
x : REAL - the solution to the system of equations in aug_A
Usage/Example:
This routine can be implemented in a program as follows
INTEGER :: n, m, i
REAL*8, ALLOCATABLE :: A(:, :), x(:)
n = 4
m = 3
ALLOCATE(A(1:m, 1:n), x(1:m))
A = RESHAPE((/2.D0, 3.D0, 3.D0, -3.D0, &
& 1.D0, -3.D0, 5.D0, 8.D0, &
& 4.D0, 4.D0, 12.D0, 4.D0/), (/m, n/), ORDER=(/2, 1/))
CALL direct_ge_bsin(A, m, n, x)
WRITE(*,*) x
The outputs from the above code:
-1.7999999999999994 -1.1000000000000003 1.2999999999999998
A comparison in computational time for direct_ge_bsin and direct_ge_bs can be implemented as follows
PROGRAM main
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER :: n(1:17), m(1:17), i, j, base
REAL*8, ALLOCATABLE :: A(:, :), x(:)
REAL*8 :: t1_i, t2_i, t1, t2
base = 0
DO j = 1, 17
n(j) = base + (j-1)*500 + 1
m(j) = base + (j-1)*500
END DO
DO i = 1, 17
WRITE(*,*) m(i)
WRITE(*,*) "-----------------"
IF (ALLOCATED(A)) DEALLOCATE(A)
IF (ALLOCATED(x)) DEALLOCATE(x)
ALLOCATE(A(1:m(i), 1:n(i)), x(1:m(i)))
CALL rand_mat(m(i), n(i), A)
CALL CPU_TIME(t1_i)
CALL direct_ge_bsin(A, m(i), n(i), x)
CALL CPU_TIME(t2_i)
WRITE(*,*) t2_i - t1_i
CALL CPU_TIME(t1)
CALL direct_ge_bs(A, m(i), n(i), x)
CALL CPU_TIME(t2)
WRITE(*,*) t2 - t1
END DO
END PROGRAM
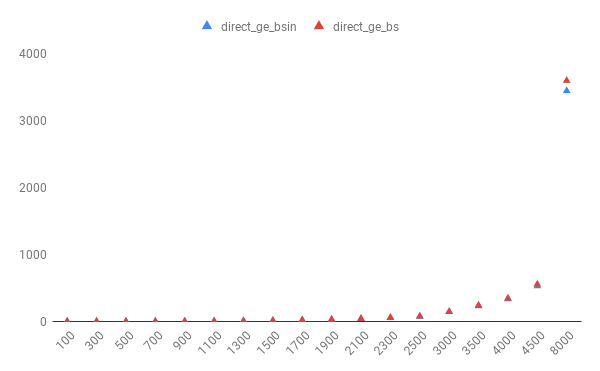
with the output seen below with the value of m given.
100
-----------------
9.5100000000000002E-004
4.6160000000000003E-003
300
-----------------
1.1191000000000001E-002
2.9197000000000001E-002
500
-----------------
7.6318999999999998E-002
0.14300099999999999
700
-----------------
0.22849000000000003
0.39683999999999997
900
-----------------
1.2918540000000003
1.5442640000000001
1100
-----------------
3.6654459999999993
3.9832510000000001
1300
-----------------
6.9960100000000018
7.5361089999999997
1500
-----------------
11.696290000000001
12.560374000000003
1700
-----------------
18.502217000000002
19.629311999999999
1900
-----------------
27.039949000000007
28.709844000000018
2100
-----------------
39.153564999999986
41.175299999999993
2300
-----------------
54.051498000000009
57.373232999999971
2500
-----------------
72.672651999999999
76.668656999999996
3000
-----------------
143.29303199999998
144.55856800000004
3500
-----------------
229.23474700000003
240.15702400000009
4000
-----------------
335.23263600000007
345.11590299999989
4500
-----------------
529.49505899999986
554.27776499999982
8000
-----------------
3441.6954460000002
3594.6079899999995
Implementation/Code: The code for direct_ge_bsin can be seen below.
SUBROUTINE direct_ge_bsin(aug_A, m, n, x)
IMPLICIT NONE
! Takes as inputs an augmented coefficient matrix, `aug_A` of size
! `m` x `n` and outputs the solution when using Gaussian Elimination
! and backward substitution, `x` of length `n`.
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: m, n
REAL*8, INTENT(INOUT) :: aug_A(1:m, 1:n)
REAL*8, INTENT(OUT) :: x(1:n)
! Initialize decrement variables and a variable to compute the sum
! of previous solutions integrated into the algorithm for the
! backward substitution method.
INTEGER :: k_b, j_b
REAL*8 :: backsum
! Initialize increment variables i, j, and k as well as a factor
! variable to be used in the row echelon algorithm.
INTEGER :: i, j, k
REAL*8 :: factor
! Executes the `mat_row_ech` subroutine inline to take `aug_A` to
! row echelon form.
! Loop across all columns except for the last (never need to touch
! that entry to cancel out what is below it). This targers the pivot
! elements
DO k = 1, n - 1
! Loop through all of the rows except for the first one to make
! them zeros using the algorithm. Makes all entries zero beneath
! the pivot element.
DO i = k + 1, m
! Calculate the factor to reduce ith row value to zero
factor = aug_A(i, k)/aug_A(k, k)
! Loop through all columns to subtract the factor multiplied
! by the previous row entry.
DO j = k , n
aug_A(i, j) = aug_A(i, j) - factor*aug_A(k, j)
END DO
END DO
END DO
! Executes the `backsub` subroutine inline to find the solution to
! the system of equations in `aug_A`.
! Calculate the last value in the solution vector `x`.
x(m) = aug_A(m, n)/aug_A(m, n - 1)
! Loop through the remaining rows in `x` to calculate the solution
! using the backward substitution algorithm.
DO k_b = m-1, 1, -1
backsum = 0.D0
DO j_b = k_b + 1, n
backsum = backsum + aug_A(k_b, j_b)*x(j_b)
END DO
x(k_b) = (aug_A(k_b, n) - backsum)/aug_A(k_b, k_b)
END DO
END SUBROUTINE